Elements, Compounds & Mixtures
Elements
 |
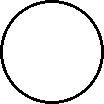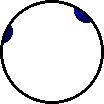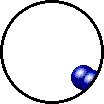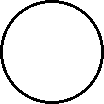 |
| Microscopic view of the atoms of the element argon (gas phase). |
Microscopic view of the molecules of the element nitrogen (gas phase). |
Note that an element:
- consists of only one kind of atom,
- cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and
- can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen).
A
molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same
element, or different elements, that are chemically bound together. Note
that the two nitrogen atoms which comprise a nitrogen molecule move as a
unit.
Compounds
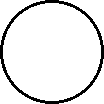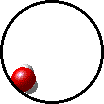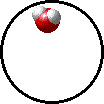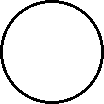 |
| Microscopic view of the molecules of the compound water (gas phase). Oxygen atoms are red and hydrogen atoms are white. |
Note that a compound:
- consists of atoms of two or more different elements bound together,
- can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means),
- has properties that are different from its component elements, and
- always contains the same ratio of its component atoms.
Mixtures
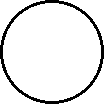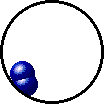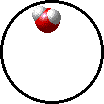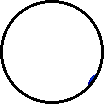 |
| Microscopic view of a gaseous mixture containing two elements (argon and nitrogen) and a compound (water). |
Note that a mixture:
- consists of two or more different elements and/or compounds physically intermingled,
- can be separated into its components by physical means, and
- often retains many of the properties of its components.
